Market Volatility and the Triggers of Investor Behavior
In the world of investing, volatility is both a constant companion and a formidable adversary. It ebbs and flows like the tide, shaping market sentiment, influencing decision-making, and testing the resolve of even the most seasoned investors. According to the 2023 Ernst and Young Global Wealth Research report, younger investors are more likely to switch into active investments during volatility, with 50% of respondents increasing allocations compared to 22% of baby boomers. Another finding of the study was 40% of wealth management clients think that managing their wealth has become more complex over the last two years, and 57% of high-net-worth individuals (HNW) who feel unprepared to meet their financial goals cite market volatility as a primary reason.
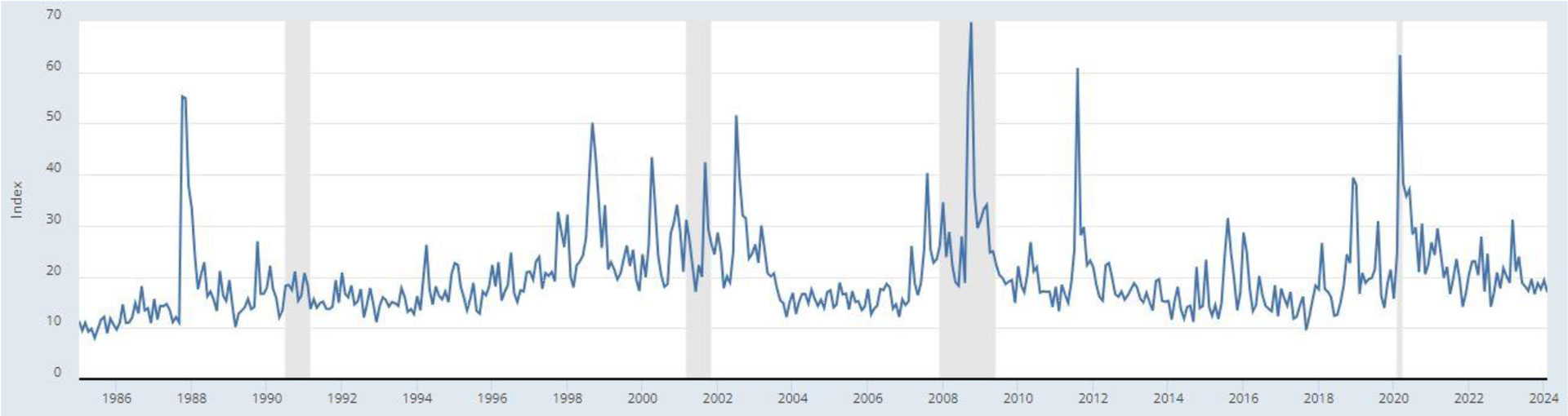
Source: FRED-St. Louis Fed Equity Volatility Tracker
Periods of high volatility are often associated with a sense of impending doom among investors. In all fairness, the evidence points in that direction as well. According to the St. Louis Fed’s equity volatility tracker, apart from the post-war recession in the early 90s, each period of elevated market volatility has been accompanied with a sustained period of economic downturn. Such history is a surefire way to spook investors.
As a result, understanding the psychology behind investor behavior during market volatility can help investors make better decisions and avoid common mistakes. In recent years, there has been a growing interest in understanding the role of behavioral finance in shaping market volatility. Behavioral finance examines how psychological biases and emotions impact financial decision-making, and when applied to market volatility, it provides valuable insights into the irrational behavior that can drive extreme price movements.
What is Market Volatility?
Market volatility refers to the frequency and magnitude of price movements in any direction for a security or market index over a specific period. Volatile stocks are generally considered riskier than less volatile stocks because their prices are less predictable. Implied volatility measures the expected volatility of the market, while historical volatility measures price changes over a predetermined period.
Volatility is an important variable in calculating option prices. The CBOE Volatility Index, also known as VIX or “Fear Index,” is a measure of investor sentiment. VIX tends to be inversely related to the S&P 500. This measures how much traders expect the price of the S&P 500 to rise or fall over the next month. A score below 20 generally indicates investor satisfaction, while a score above 30 indicates concern.
It is important to remember that even though market volatility makes the most seasoned investor think deeply about their choices, it is a normal characteristic of all financial markets.

Notable Events of Heightened Market Volatility
There have been numerous instances in the past where market events have led to sustained periods of elevated market volatility. Some of the major events include:
- Black Tuesday (1929) and the Great Depression
The stock market crash of 1929 signaled the beginning of the Great Depression. The sharp decline in stock prices led to panic selling as investors rushed to liquidate their holdings. This behavior was driven by a lack of trust in the market and fear of further losses. The lessons from this period highlight the importance of understanding the psychological factors that can trigger extreme market movements.
- The Oil Crisis (1973-1974)
The Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) imposed an oil embargo in response to U.S. support for Israel during the Yom Kippur War, leading to a sharp rise in oil prices and triggering a period of stagflation (high inflation and stagnant economic growth) in the U.S. - Dot-com Bubble (2000)
The rapid rise and subsequent collapse of technology stocks in the late 1990s and early 2000s became an example of a speculative bubble. Investor enthusiasm and irrational expectations have led to sharp corrections after stock price rises. The results highlight the risk of overestimation and the importance of performing careful fundamental analysis. - Global Financial Crisis (2008)
The global financial crisis was triggered by the bankruptcy of Lehman Brothers in 2008. Investor behavior during this period was characterized by widespread panic as financial institutions faced liquidity shortages and markets experienced extreme volatility. The crisis has highlighted the interconnectedness of global financial markets and the potential for systemic risks to amplify market volatility. - COVID-19 Pandemic (2019)
In early 2019, the COVID-19 pandemic led to a sharp and severe market downturn. Fear and uncertainty have led to massive selling across asset classes. However, central bank intervention and government stimulus have helped stabilize markets, demonstrating the impact policy decisions have on investor sentiment.
These historical examples demonstrate that investor behavior during stock market fluctuations is influenced by a combination of psychological factors, market conditions, and external events. Although it is difficult to predict the timing and severity of market fluctuations, understanding behavioral trends that may occur during these periods is important for investors seeking to make informed decisions.

The Traits and Behaviors of Investors During Times of Uncertainty
Stock market fluctuations, a subset of financial market volatility, have been a subject of extensive research due to their profound impact on investor behavior. Understanding the relationship between these fluctuations and investor behavior provides insights into market dynamics, risk management, and decision-making processes.
One prominent theory explaining stock market fluctuations is the Efficient Market Hypothesis (EMH), which posits that stock prices always reflect all available information. According to EMH, market participants process information rationally and adjust their investment decisions accordingly. However, this is clearly not applicable during times of high uncertainty. By virtue of the state of affairs, it is impossible to make efficient forecasts about the market. In a situation of high market volatility, EMH is not only inefficient, it could also feed into the false euphoria of investors stemming from an unfounded confidence in their knowledge base.
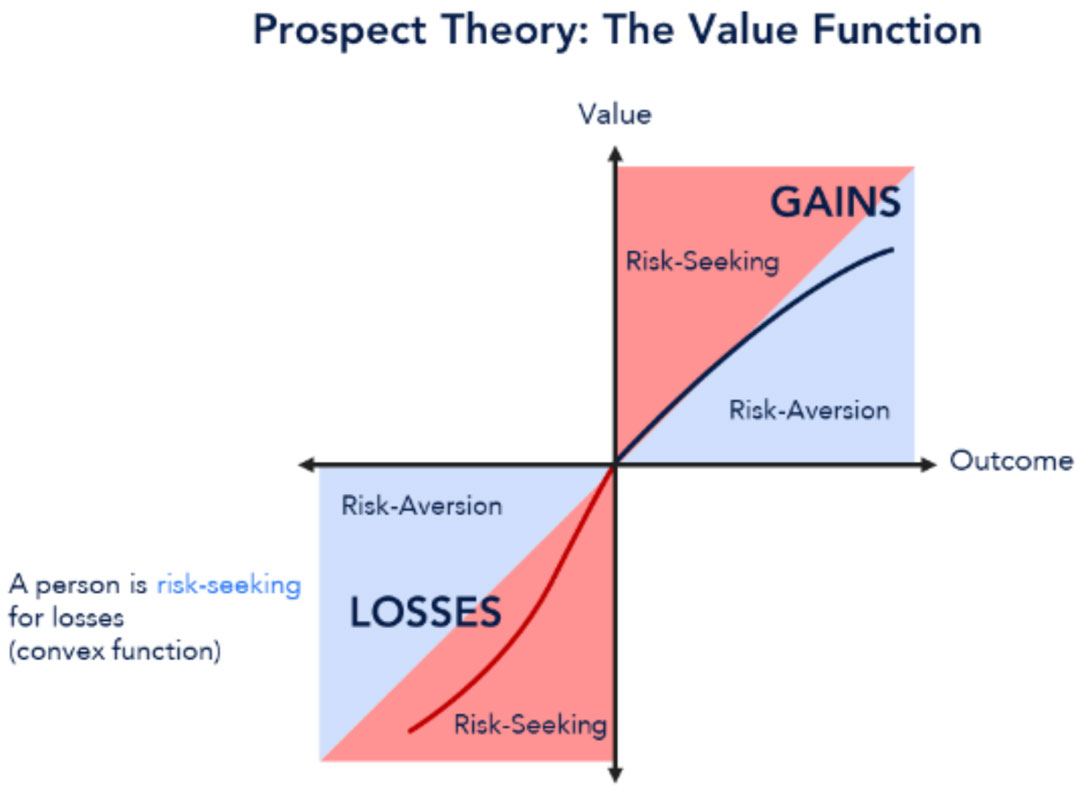
Prospect theory is another behavioral science theory that can help understand (not justify or predict) the behavior of investors during times of heightened volatility. Daniel Kahneman and Amos Tversky’s path breaking research tries to understand investor behavior during times of experiencing gains and losses. Loss aversion is one of the most salient features of this theory as the theory states that the feelings associated with loss are stronger than the positivity associated with a gain. In the context of the stock market, investors are prone to keep losing stocks, hoping they will rebound, and are more likely to sell gaining stocks, afraid of a potential downturn. The theory presents the potential rationale behind incongruous investor behavior and their emotionally driven probability association to different potential outcomes, based on the kind of losses or gains they have faced in the past.
Overall, investor behavior during periods of high market volatility can be largely characterized by certain patterns:
- Disposition Effect:
As mentioned before in the discussion about Prospect Theory, investors tend to hold onto losing investments for too long while quickly selling winning investments. This behavior can be exacerbated during volatile periods when emotional reactions are heightened even further. - Flight to Safety:
During heightened volatility, investors might shift their investments from riskier assets to safer ones, such as government bonds or gold. This flight to safety reflects a desire to preserve capital in uncertain times. - Herding Behavior:
Investors may follow the actions of the majority, leading to herding behavior. This can amplify market movements, both up and down, as investors rush to mimic the actions of others. It can be said that the sudden increase in money market fund investments can be attributed to this kind of behavior. - Overreaction and Underreaction:
Behavioral biases can lead investors to overreact or underreact to market news. Overreaction occurs when investors exaggerate the impact of news, causing excessive price movements. Conversely, underreaction is observed when investors fail to fully incorporate new information into their decisions. - Selective Perception:
Investors might focus on information that confirms their existing beliefs while ignoring contradictory information. This can lead to misjudgments during periods of high uncertainty.
The impact of investor behavior on stock market fluctuations can also create a feedback loop. Investors’ reactions to market volatility can exacerbate price swings, causing further uncertainty and influencing subsequent behavior. Market sentiment, driven by investor behavior, can become a self-fulfilling prophecy, where widespread fear or exuberance influences trading decisions and subsequently impacts market prices.

The Rise and Fall of the Most Recent Period of Volatility
Markets often experience periods of increased volatility. Investors should typically expect volatility to be around 15% of the average return in a year. Market volatility was particularly quiet in 2023, a stark contrast to the prior year. With inflation declining and the Fed pausing interest rate hikes, the volatility of the S&P 500 in 2023 was less than two-thirds of its historical average over the 10 years from 2013 to 2022.
However, there were a few notable spikes. During the U.S. regional banking crisis in March, the VIX jumped above 30 amid heightened investor panic about bank profitability. Later in May, volatility spiked again after the Fed raised rates for the 10th time as it began speculating on a ‘higher for longer’ rate scenario.
The VIX fell to a four-year low in December 2023 after the Fed announced it would cut interest rates in 2024. Investors are closely watching how macroeconomic and geopolitical uncertainties will unfold during 2024. Moderating inflation, solid consumer spending, and labor market strength eased investor concerns in 2023, leading to lower volatility towards the end of the year. This is no guarantee that volatility will not return in 2024, as many geopolitical, trade and monetary policy decision could play tricks with investor’s thinking and decision-making once again.
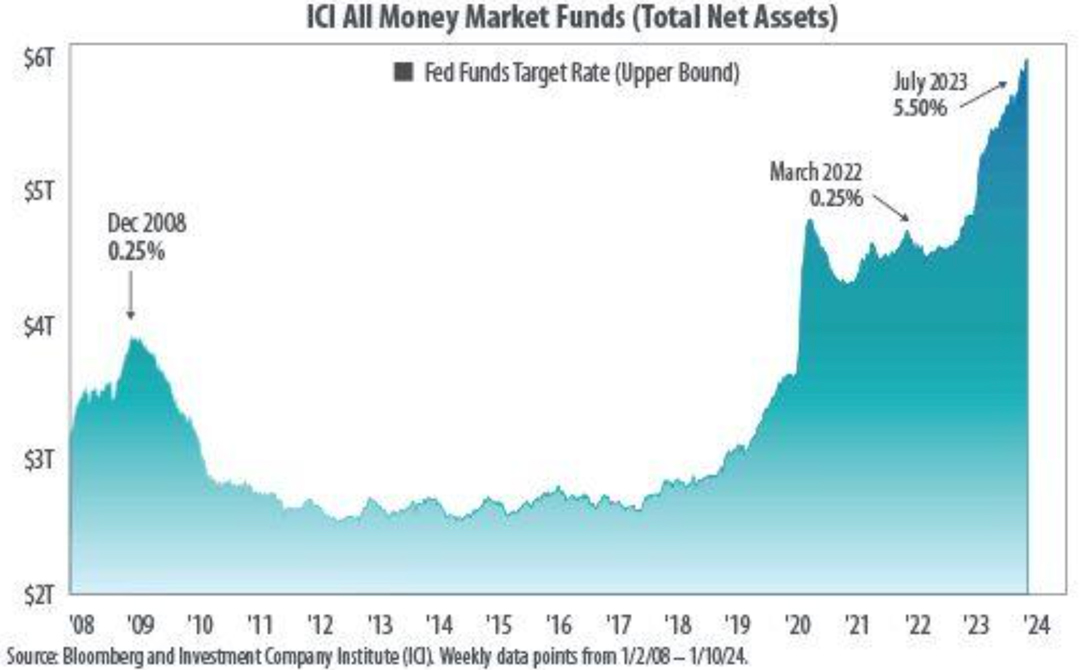
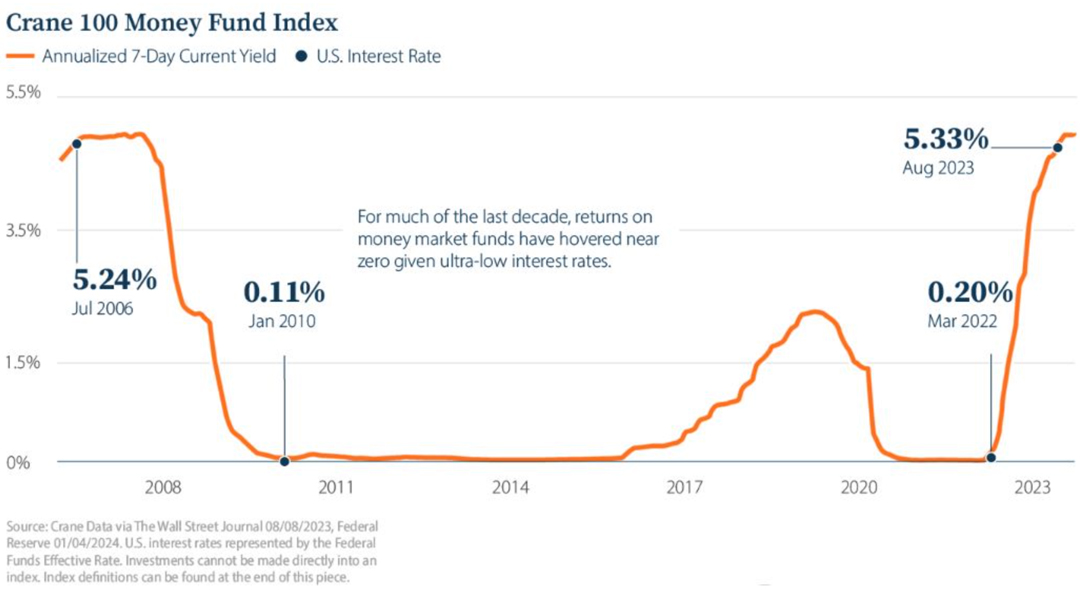
A telling sign of how investors still do not believe that there is no clear path to follow is their preference to hold cash and cash-like instruments, rather than invest in securities or bonds. Money market funds typically hold short-term assets including government debt, whose yields climb or fall rapidly depending on the central bank’s stance on monetary policy. Almost $1.19 trillion has flooded into U.S. money market funds through December 2023. That is a far cry from negligible inflows in 2022 and well above the average full-year net inflow figure of $179 billion for 2012-2022. As recently as March 6, 2024, U.S. money-market funds, bringing total assets to $6.08 trillion. These funds are considered safer in times of volatility and this is a clear sign that investors believe there is more uncertainty to come.
While some argue that volatility could remain subdued, others believe it could rise again in 2024 due to overheating markets and credit market pressures.

Ways to Navigate a Volatile Market
To mitigate the impact of cognitive biases on market volatility, investors can employ several strategies. First, awareness is key. Recognizing and acknowledging the existence of biases can help investors take a more rational and objective approach to decision-making. Second, diversification can help reduce the impact of individual biases by spreading investments across various asset classes. Additionally, seeking out diverse sources of information and opinions can help counteract confirmation bias and provide a more balanced perspective.
There are certain tenets that can help investors navigate such times of severe uncertainty. The effectiveness of these tenets, however, depend completely on how disciplined investors can be in their implementation. At Howard Capital Management (HCM), these tenets have helped to build the foundation for growth as well as downside mitigation over many decades. A non-emotional, math-based approach to investing and market analysis has formed the basis for the proprietary system called the HCM-BuyLine®, which is the backbone of all investment strategies offered by HCM.
For the average investor, these tenets could help them avoid making novice mistakes and act while keeping in mind their final goal.
- Seek to avoid major losses through risk management:
Overlaying investments with a risk management strategy can potentially help identify major market downturns to avoid portfolio devastation. - Seek to implement a math-based strategy:
The rise of computerized trading is consequently making investing more challenging. With a math-based and quantitative strategy, investors can seek to move in and out of the market faster, striving to minimize losses and maximize gains. - Move to cash/lower volatility investments during major market declines:
It could take months or even years to recover from devastating losses. Investors who avoid much of a significant drop by moving to safety not only attempt to preserve assets in major market declines, but positions themselves ready to capture major upturns (and potentially at attractive prices). - Seek to remove emotion from the equation:
Investors can be emotional with the swings of the market — holding a stock as it falls or selling it before it reaches its full potential can wreak havoc on a portfolio. An emotional approach to investing can hinder the ability to effectively manage investments. - Stay the course:
Commit to a strategy and risk level that not only could help one sleep soundly at night, but also with the objective of meeting current income needs and long-term financial goals.
Resources:
Sources:
- https://www.valuethemarkets.com/analysis/money-market-fund-assets-reach-new-record-high-as-rate-expectations-rise
- https://www.ft.com/content/e3e5ad22-64b3-43f5-8592-eb21bb83f289
- https://www.jetir.org/papers/JETIR2009472.pdf
- https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/EMVOVERALLEMV
- https://www.ey.com/en_gl/newsroom/2023/04/investor-behavior-changes-in-face-of-increasing-market-volatility-as-demand-shifts-to-active-investments-and-fintech-new-ey-report-finds
- https://fastercapital.com/content/The-Intersection-of-Behavioral-Finance-and-Market-Volatility.html
- https://howardcm.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/2024-HCM-VMG-HCM-021324-025-web.pdf
- https://howardcm.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/The-Pitfalls-of-Emotional-Investing_Updated_HCM-091923-103-WEB.pdf
- https://www.hartfordfunds.com/practice-management/client-conversations/managing-volatility/10-things-you-should-know-about-volatility.html
- https://www.forbes.com/advisor/investing/what-is-volatility/
- https://www.investopedia.com/terms/v/volatility.asp#:~:text=In%20the%20securities%20markets%2C%20volatility,factor%20when%20pricing%20options%20contracts
- https://www.fidelity.com.sg/beginners/your-guide-to-stock-investing/understanding-stock-market-volatility-and-how-it-could-help-you
- https://fastercapital.com/topics/the-psychology-of-investor-behavior-during-volatile-times.html
- https://www.imf.org/en/Blogs/Articles/2024/01/31/emerging-markets-navigate-global-interest-rate-volatility
- https://www.visualcapitalist.com/sp/market-volatility-in-2023/